Search Techniques
Research Topic into a Research Question
Hone down a broad research topic/interest into a research question/query that your work will address.
Example: "How did the death of Sitting Bull impact the Lakota legacy of the Standing Rock Reservation?"
Formulating Keywords/Search Terms
Break down your research question into searchable terms that will retrieve a variety of results
Example: Sitting Bull, Lakota, Standing Rock Reservation
Using Synonyms and Related Terms
Generate a list of related terms/synonyms that can expand or narrow your search
Example: Native Americans, the Dakotas, Standing Rock Agency
Using Boolean Operators and Other Techniques
See how to use Boolean Operators on this page
Other techniques can be employed to make your searching more efficient:
Quotation Marks will allow you to search for an exact phrase as it appears in order
Example: "Lakota tribe" "Standing Rock"
Truncation and Wildcards are handy for locating similar but not indentical terms
Note: Google automatically truncates/stems searches
* Example: *east will find Northeast and Southeast - this replaces all the preceding or remaining letters
# Example: wom#n will find woman and women - this replaces one character in the middle or at the end of a word
? Example: col?r with find color and colour - this will search for different spellings of a word
Specific Site Searching
Precede your search with site: if you know you want results from a specific place or from a type of site (.org, .edu, .gov)
Example: op-ed site:nytimes.com
Example: COVID restrictions site:.gov
Putting These Together
An efficient, well organized search query may look something like this:
"Sitting Bull" AND (Lakota OR Hunkpapa) AND "Standing Rock" site:.org
Digital Literacy Vocabulary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Algorithm | A set of step-by-step instructions or rules to solve a problem. |
| Bias | A preference for or against something that can impact how information is presented. |
| Clickbait | Content designed to attract attention and get people to click on a link. |
| Credibility | The quality of being believable and trustworthy. |
| Digital Citizenship | The skills and knowledge used to effectively, responsibly, and safely use the Internet and other digital technologies. |
| Digital Footprint | The record of your online activity that can be viewed by others. |
| Disinformation | False information spread on purpose to deceive people. |
| Evaluate | To carefully examine something in order to judge its value or quality. |
| Filter Bubble | A situation where you may only see information that agrees with your existing views. |
| Misinformation | False information that is spread, regardless of intent. |
| Source | The origin of information or where something comes from. |
| Verify | To confirm that something is true or accurate. |
The Research Process
Step 1: Identify your research topic and begin formulating a thesis/research question
Step 2: Do basic general research to build your knowledge and understanding and focus your thesis/question
Step 3: Locate and read materials and sources needed to support your writing
Step 4: Evaluate materials and sources for evidence
Step 5: Take notes on the evidence you will integrate into your research
Step 6: Write your paper/complete your project with corresponding in-text citations
Step 7: Complete your bibliography and include it at the end of your work
Boolean Operators
Use AND in a search to narrow results - this tells the database to include all of the terms in search results
Example: liberation AND theology AND socio-economic
Use OR in a search to broaden results - this tells the database to retrieve any of the terms in the search results
Example: liberation OR theology
Use NOT in a search to exclude (narrow) results - this tells the database to ignore/remove search results that include these terms
Example: womanist NOT feminist
If you are using AND and OR together in a search query, enclose the OR terms in paranthesis for the database to make sense of the order of your search
Example: (liberation OR womanist) AND theology
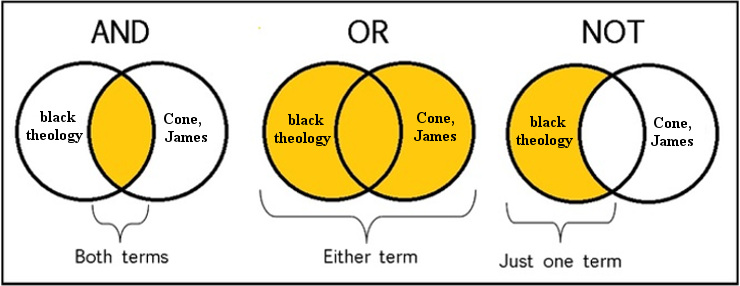
Boolean operators Venn diagram. The Styberg Library, Garrett-Evangelical Theological Seminary, 8 Jan. 2025, guides.garrett.edu/atlaresearchguide. Accessed 17 Jan. 2025.
Source Types
Primary Source
- First hand account or direct evidence
- Documentation that is orignial to an information event or a person, without interpretation
- In art, this is any original artistic piece
Examples: Sculptures, paintings, diaries, letters/correspondence, fiction books, speeches
Secondary Source
- Analysis, interpretation, or evaluation of original events, research, or documents
- Use (and often quote) primary sources and other evidence sources for context and examination
Examples: Journal articles that review or interpret research, textbooks*, edited works, commentaries, political analysis
Tertiary Source
- Generally these are reference sources that index, organize, summarize and repackage information
- These are usually not credited to a specific author
Examples: Dictionaries, encyclopedias, almanacs, guidebooks, handbooks, manuals, textbooks*
